Abstract
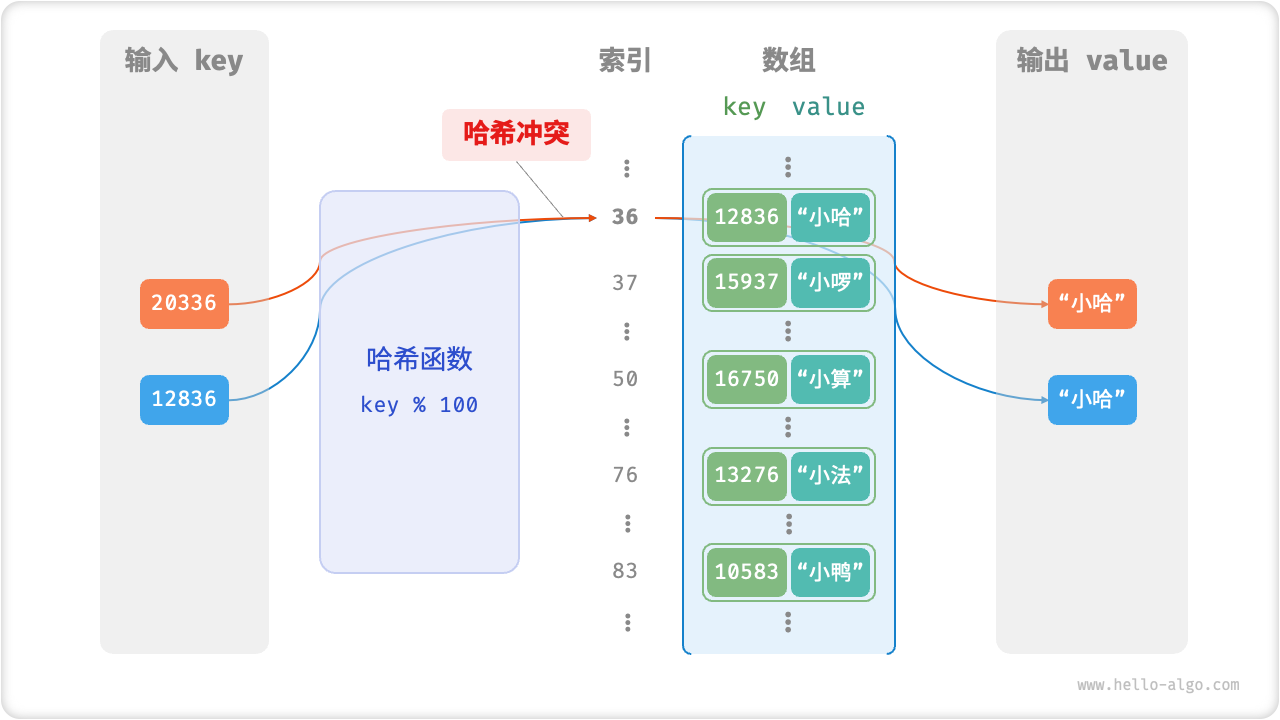
- Occurs when Hash Function on two different inputs and produces the same output
- In the above example and result in the same value
Hash Map Expansion
- Expand the output space to avoid Hash Collision totally if expansion is big enough
- Reduce the chance of hash collision if expansion isn’t big enough
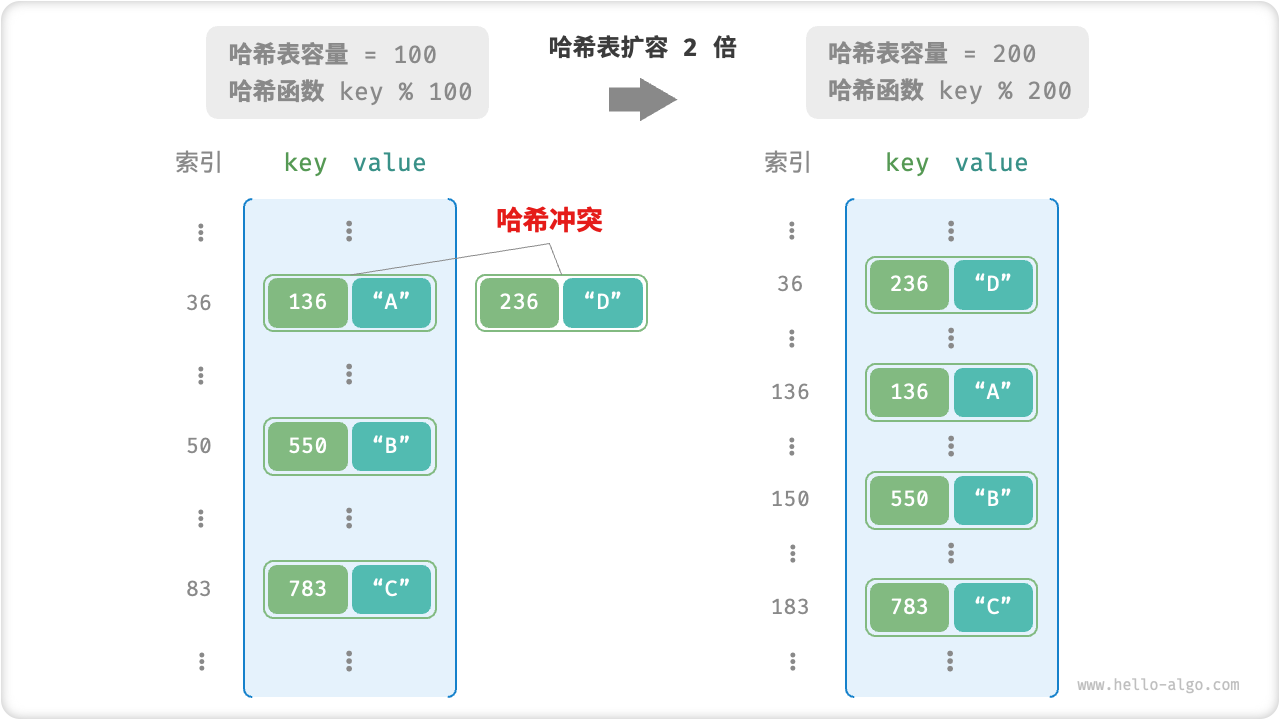
- In the above example, when and result in the same output , we can double the output space to avoid the collision
- After expansion, ,
Load Factor
- A faction of total elements inside Hash Map and Total buckets
- Measure the severity of Hash Collision
- Triggering condition for Hash Map Expansion
Java
- When Load Factor exceeds
0.75, Hash Map Expansion will be triggered to expand twice the original size
Hash Map Expansion Cons
- However, with the change of the output space size, it requires us to re-run the Hash Function on all values to obtain the new Bucket
- And it is very time consuming to move all key-value pairs from old arrays to new arrays & recalculating hashes
- Thus, we will reserve a pretty decent space to avoid frequent expanding
Separate Chaining
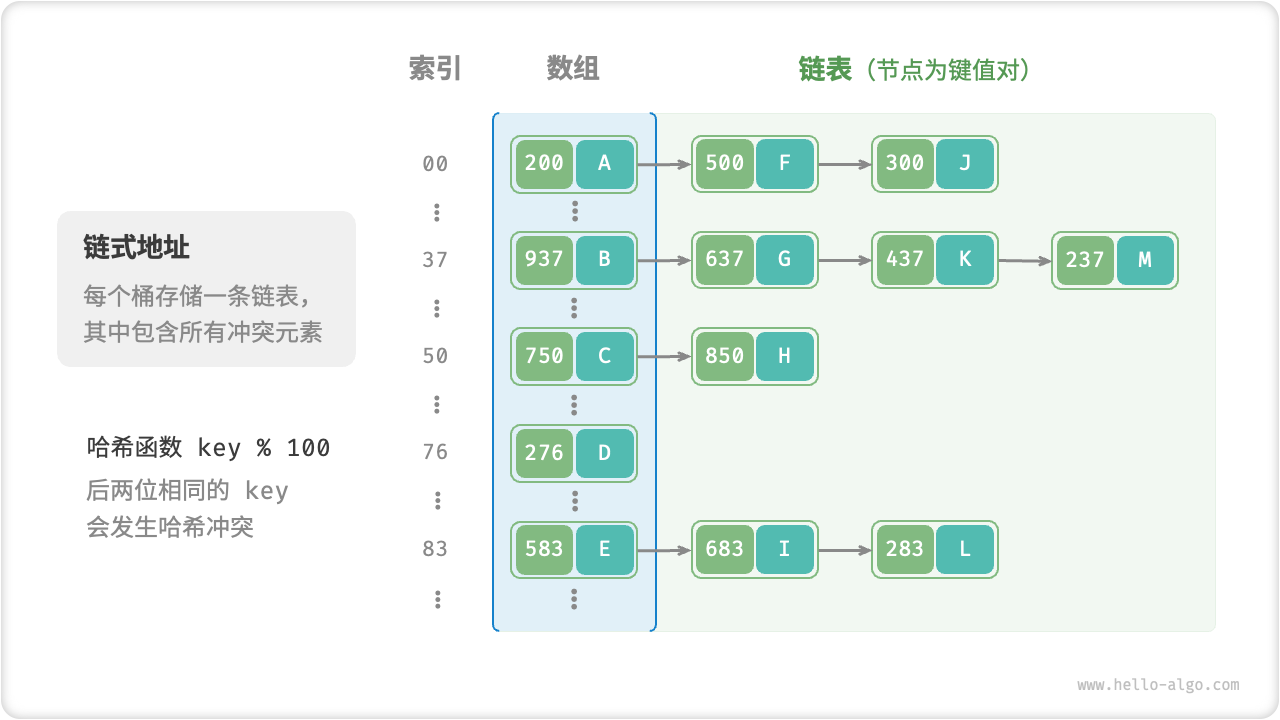
- Use each Bucket in the underlying output space of Hash Map to hold a Linked List node
- We put all the conflicted key-value pairs as nodes in the Linked List, we can live with a certain degree of Hash Collision and reduce the frequency of Hash Map Expansion
- You can find a separate chaining code implementation here
Java
- Starting from JDK 1.8, when Hash Map length reaches 64 & the Linked List length is 8. Linked List will be converted to Red Black Tree to improve performance
Golang
- Every Bucket has maximum 8 key-value pairs. Once exceeded, it will be linked to a overflowing bucket
- When there is too many overflowing buckets, Hash Map Expansion will be performed to ensure performance
Mechanism
Search key-value pair with key
- Obtain the index of Bucket by passing the key to the Hash Function
- Obtain the starting node of the Linked List with the index
- Iterate through the Linked List to find key-value pair node that matches with the given key
Add key-value pair
- We perform Search key-value pair with key to ensure it is a new key-value pair we want to add
- If unable to find, we add a new node with the key-value pair to the Linked List. Else we return duplicated key error
Delete key-value pair
- We perform Search key-value pair with key to ensure the key we want to delete exists
- Delete the key-value pair node if there is one
Separate Chaining Cons
-
More Main Memory usage
-
Because each key-value pair node needs space to store a pointer to point to the next node
-
Reduced search efficiently when Linked List is getting long, since searching on Linked List is linear, not constant
-
We can converted the long Linked List to AVL(Balanced Binary Search) Tree (平衡二叉搜索树) or Red Black Tree to optimise the search efficiency from
O(n)toO(logn)
Open Addressing
-
Similar to Separate Chaining, it is an approach to live with Hash Collision, so as to reduce the frequency of Hash Map Expansion
-
But unlike Separate Chaining, open addressing doesn’t leverage on a Linked List to live with
-
2 approaches - Linear Probing and Double Hashing
Delete key-value pair
We need a special indicator to remove a key-value pair. If we just make it empty, the key-value pairs stored after it will be ignored when we are trying to search a key-value pair that has Hash Collision with the deleted key-value pair
