Abstract
-
Decides on hardware allocation and management with regard to software
-
MacOS’s kernel is XNU
-
Windows’s kernel is NT Kernel
Kernel Booting
- Get configuration info from BIOS
- Check for missing Device Driver
- Start up Init System
- Initialise Page Table
- Starts up OS System Program
- OS is booted up and ready to be used by the User
Kernel Architecture
Micro Kernel Architecture
- Kernel only handles critical part of the system. The rest runs in User Space
- Different kernel components communicate with each other via Inter-Process Communication (IPC)
- Used by MINIX
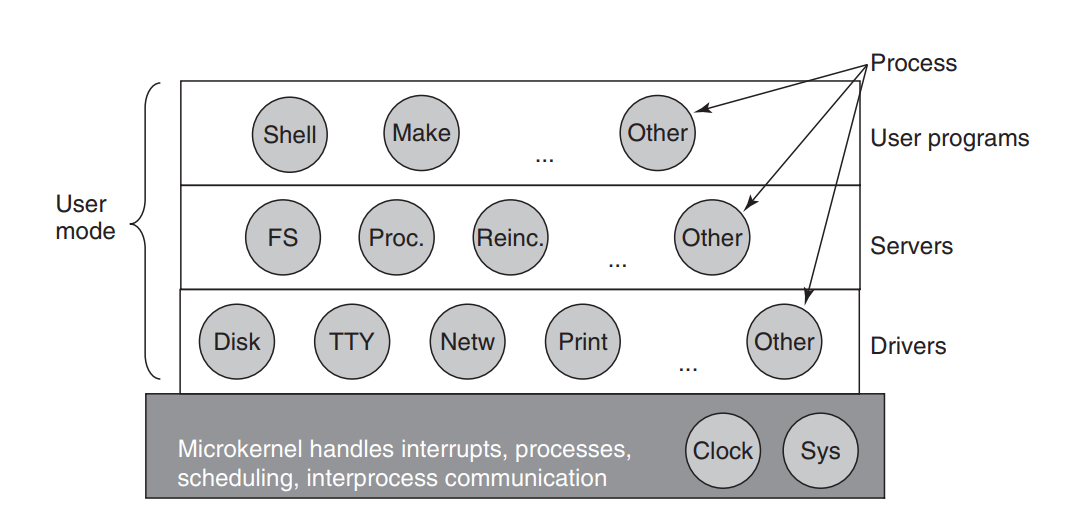
Process (进程) crashes, it doesn't crash the entire system
Lower performance due to the overhead of communication between different modules
Monolithic Kernel Architecture
- By far, the most common Kernel architecture, used by Linux
- The entire kernel runs as a single program in Kernel Mode
- Consist of a collection of Procedures, linked together into a single large executable binary program. Each Procedures in the system is free to call any other one
Very efficient to have the ability to call any of the procedures
But having thousands of Procedures that can call each other without restriction may also lead to a system that is unwieldy and difficult to understand
A crash in any of these Procedures will take down the entire Kernel
Terminologies
Preemptive Kernel
- Kernel that can be interrupted and scheduled just like Process (进程) in the User Space
CPU, and slow down user space process
